
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been estimating the global burden of disease attributable to a risk factor using the described approach since about two decades (e.g., (4)). 2002: Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease GBD 2016 Risk Factor Collaborators, 2017: Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016Įzzati et al. WHO, 2009: Global health risks: Mortality and burden of disease attributable to selected major risks The attributable disease burden is then estimated by multiplying the total burden by the PAF for each age, sex, and relevant disease group. the population attributable fraction (PAF), as described above, based on the distribution of the population into the various exposure levels for a risk factor, including the counterfactual exposure level, and the relative risk linking exposure and disease or other health outcomes.the counterfactual level of risk factor exposure which usually corresponds to an exposure where a minimum risk is incurred,.disease statistics for the population for the metric of interest (number of deaths, years of life lost, years lived with disability, or disability-adjusted life years ),.The following ingredients are used for estimating the attributable disease burden: doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6.Ĭomparative risk assessment methods are the preferred methods used to estimate the burden of disease in a population attributable to a risk factor. 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborator (2018) Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories. WHO, 2003: Quantifying environmental health impacts: Introduction and methods WHO, 2004: Comparative Quantification of Health Risks Only RRs from studies of high quality epidemiological should be used in such assessments. These formulas assume no confounding or effect modification. The counterfactual exposure distribution is the exposure level with no or very low disease risk (i.e., RR of 1).Ī simplified formula applicable to only two levels of exposure (exposed and unexposed) is the following (3): Where pi is the proportion of the population exposed at exposure level i, p'i is the counterfactual exposure distribution and RRi is the relative risk at exposure level i.

It can accommodate several exposure levels which a population can be exposed to (2): The RR provides the ratio of the probabilities to get a certain disease or to die due to a disease when two differently exposed groups are compared.Ī common form of the formula for estimating the PAF is the following.

Two types of information are needed to estimate the population attributable fraction (PAF): Following the well-established method outlined below, disease burden from different risk factors such as lack of physical activity, smoking or air pollution can be calculated and compared and changes over time (for example after an intervention that reduced air pollution) can be assessed.
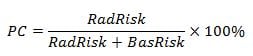
This requires an integration of knowledge about the “dangerousness” of a risk factor (this is usually assessed as the relative risk for a specific disease-risk factor combination) and the “frequency and level of exposure” (how many people in a population are exposed to which quantities of the risk factor). To this end, it is necessary to quantify the burden caused by diseases and injuries which can be attributed to known risk factors in a comprehensive and comparable way. For many health policy decisions regarding prevention and intervention, it is important to know which risk factors are most important for population health, so the available resources can be spent most efficiently to improve the health of entire populations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
